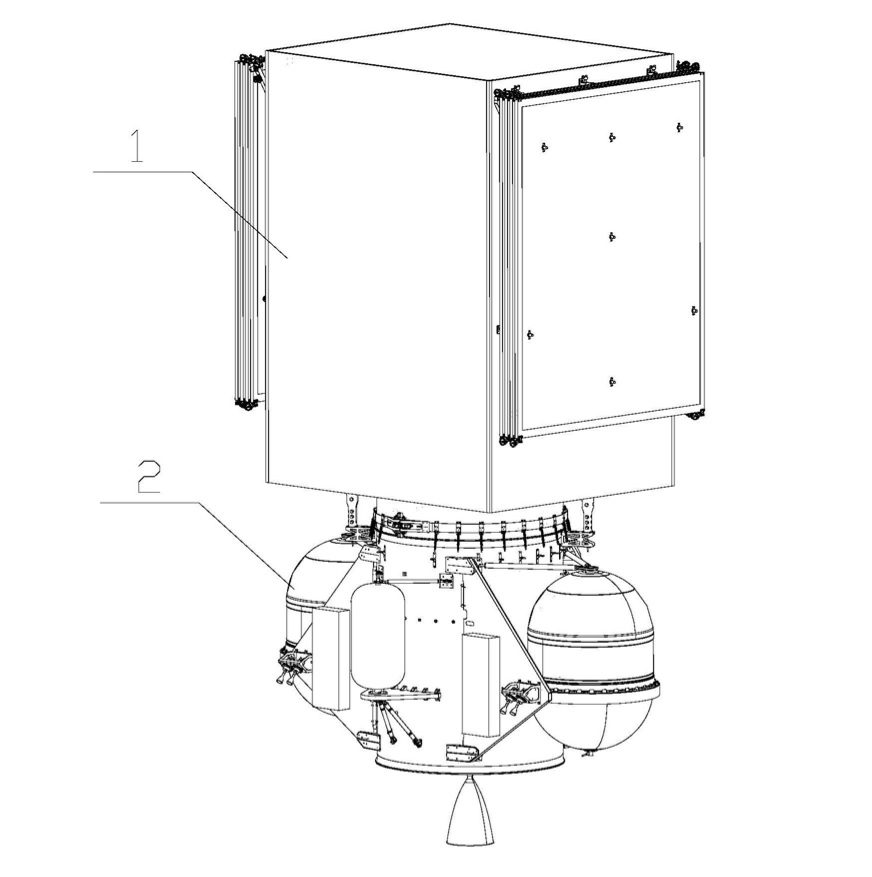
The APT Satellite Holdings-owned APSTAR 6E HTS communications satellite, which was placed into an initial orbit by a Chinese Long March 2C/3 (CZ-2C/3) rocket on 12 January, has reportedly run into problems.
The launch, from the Xichang site, was unusual in that it employed such a small rocket to make the launch of the 1,800 kg satellite. To make this work, the CAST-built DFH-3E bus satellite was equipped with a detachable propulsion module called the SPS, which was supposed to manoeuvre the spacecraft into an initial partial transfer orbit. From here the satellite’s electric propulsion system was due to take over to raise and circularise its orbit into a geostationary Earth orbit over 134 degrees East, where it would operate.
Raising the satellite into position was expected to take 10 months. However, it may now take several weeks longer as the SPS main engine is reported not to be working after a series of valve faults involving the pressurisation system. While these have been worked around, it seems that another fault has prevented the ignition of the SPS main engine.
It is understood that the APSTAR 6E satellite has 10N conventional thrusters which will now be used instead of the main engine to achieve the initial orbital raise. This will be followed by a raising and circularisation operation by the electric thruster system, which will also be used for operational stabilisation once on station. No significant loss of lifespan is expected, and hence no insurance loss, for Apstar 6E satellite which is reportedly insured for circa US$150 million.
Update on 19 January: Having been in a 646 x 232 km orbit at 28.5 degrees inclination, the APSTAR 6E satellite has now begun its back-up orbital raising procedure.