An Antares 230+ rocket operated by Northrop Grumman lifted off from the Wallops Island launch site in Virginia, USA, at 1032 GMT on 7 November. On board was a Cygnus NG-18 freighter spacecraft headed for the International Space Station (ISS) on a cargo mission for NASA. The spacecraft had been named S.S. Sally Ride after the former scientist and astronaut. Some 3,700 kg of cargo was aboard. Also aboard were three “Bird” programme CubeSats (Zimsat, Taca, PearlAfricaSat-1) which were due for later release from the ISS.
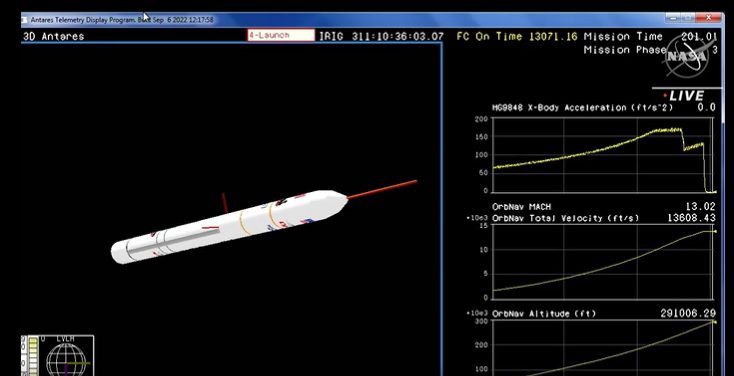
Acceleration telemetry shows clearly the points of main engine cut offs (one seems a second or so ahead of the other) for the Antares 230+ launch of Cygnus NG-18 (Sally Ride). Courtesy: NASA TV
After the initial burn, the first orbit was 334 x 228 km at 51.7 degrees inclination. After raising itself further, the spacecraft was expected to dock with the ISS later on the same day.
The Antares rocket series only has one launch left: another Cygnus flight: Cygnus NG-19. This is because of a necessary redesign to avoid having to use Russian rocket engines. The current Antares rocket employs a pair of Russian-made RD-181 engines on its Ukrainian-built first stage. A new rocket to replace Antares has been dubbed MLV. It is currently being designed and may have a reusable first stage.
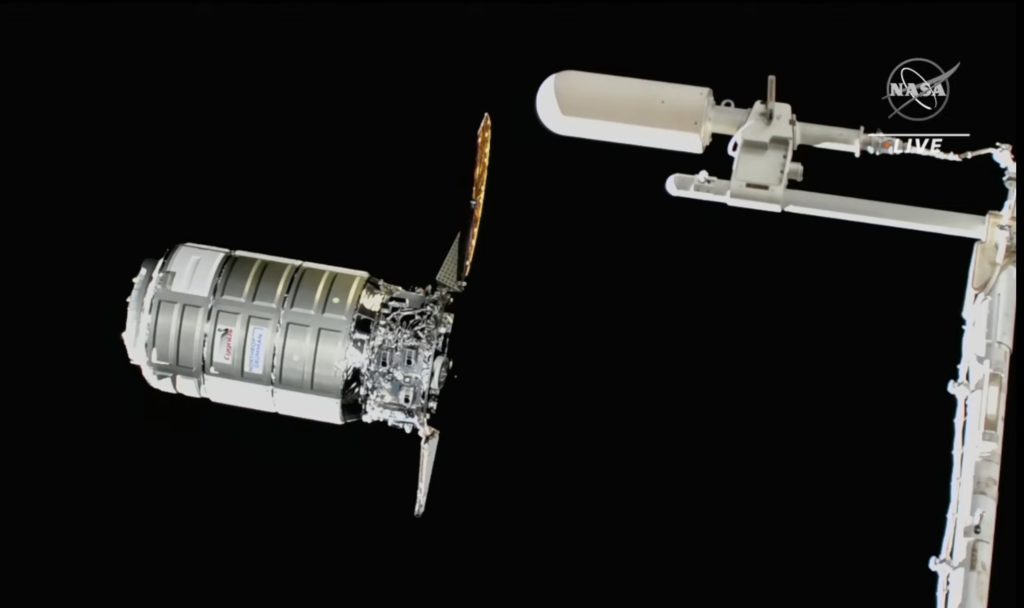
“Wounded bird” Cygnus NG-18 with only one of its arrays out approaches ISS. It was successfully grappled and berthed by the ISS robot arm. Courtesy: NASA TV
Update on 10 November: It was later announced that one of the two solar arrays on the Cygnus craft was stuck and had failed to deploy. NASA later confirmed that there would be enough power to allow an approach to the ISS, and on 9 November this was achieved, followed by the spacecraft being grappled and berthed by the ISS robot arm. Space insurers will be relieved as the delivery mission was insured for US$40 million. The staged risk cover does not end until the craft is successfully released from the ISS.
With respect to what caused the anomaly, Northrop Grumman noted that the jammed solar array deployment resulted from debris from an acoustic blanket lodging in the deployment mechanism during one of the Antares staging events. This may or may not be the apparent strange launch event shown by the mission animation and telemetry measurements of acceleration, velocity and direction. Specifically, at one point the thrusters apparently fired to point rocket stage in the wrong direction before fairing release. This was followed by an apparent thruster correction to the attitude AFTER the upper stage solid rocket engine started to fire. A view from the ground sees a spectacular fiery turn.
Here is the animation.https://youtu.be/X-R0qj7EWj8
Graphical glitch? Intended maneuver? Cygnus made it to orbit after this interesting staging animation during the Antares launch. pic.twitter.com/BkBNkbWSb8
— Michael Baylor (@nextspaceflight) November 7, 2022







