Dr Benjamin (Ben) Carlson, Senior Research Scientist at Intelligent Automation Inc., has notified Seradata of an error on the SpaceTrak database with respect to the likely cause of an anomaly to the GOES-4 spacecraft in 1982.
The original report noted that a surface Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) resulted in the spacecraft’s Visible Spin Scan Radiometer-Atmospheric Sounder (VAS) failing at 0445 GMT on 26 November 1982, and that this was probably caused by high energy protons from an X-class solar flare.
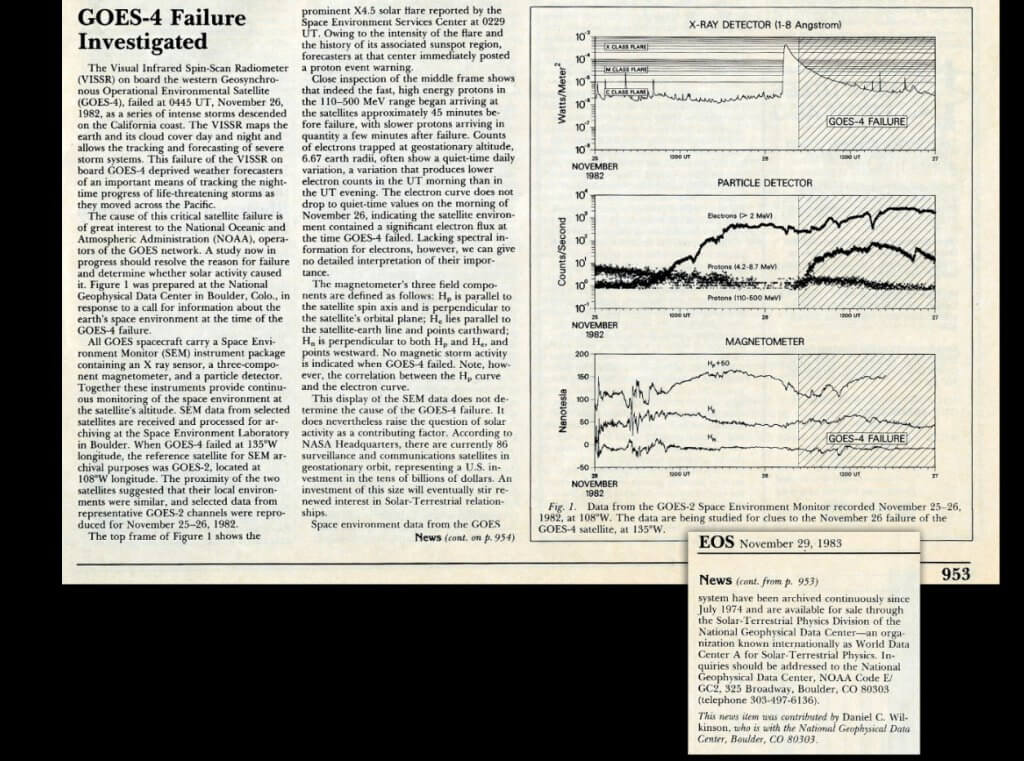
EOS magazine report of GOES 4 anomaly cause…but the charts show that it was the electrons not the protons that probably did it. Courtesy: EOS
Following discussions with officers at NOAA and The Aerospace Corporation, Carlson points out that such an ESD-caused failure was much more likely to have been caused by the arrival of high energy electrons. Ben Carlson went on to examine a report from the EOS magazine which made the same error even as it published charts showing the space weather at the time (from detectors on GOES-2 close by). They clearly show that there was a large environmental rise in high energy electrons when the GOES-4 VAS failure took place (the high energy protons had started to arrive by then but peaked several hours later).
Our thanks to Ben Carlson. We have now amended this event to show that it was the arrival of high energy electrons and not protons that was the likely cause.






