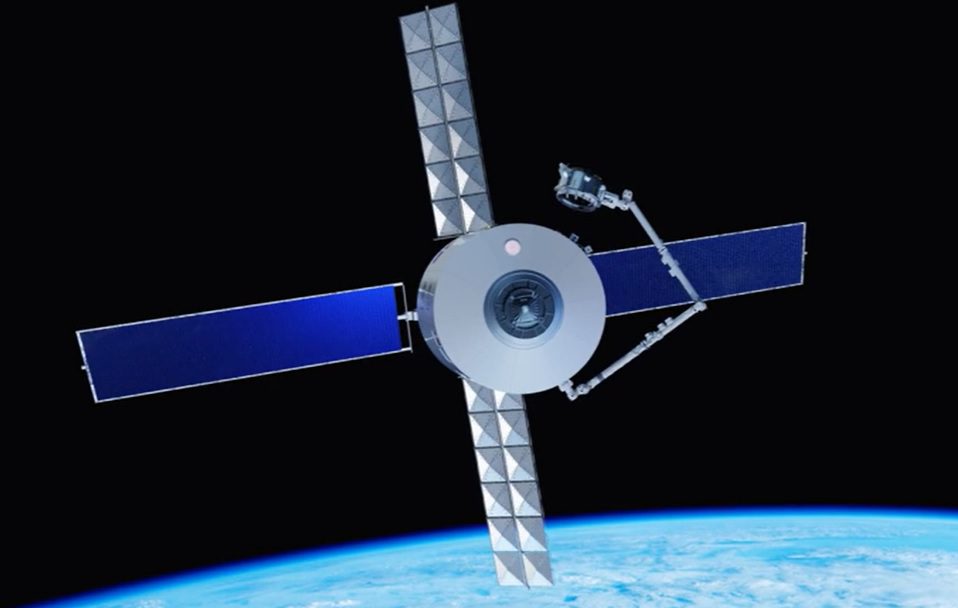
The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)’s rocket and spacecraft development establishment, the Tsukuba Space Center, has produced a concept for a four-crew capsule that is part of a Mitsubishi Heavy Industries H-IIB rocket launched spacecraft consisting of four modules, the Launch Escape System (LES), Manned Re-entry Module (MRM), Orbital Habitation Module (OHM) and Propulsion Module (PM)
Designed for LEO missions the JAXA’s 2025 vision includes a Japanese human spaceflight capability and the concept work has been drawn up in preparation for possible formal design cycles
The spacecraft is a 16,800kg (36,960lb), 4m (13.1ft)-diameter vehicle that would use systems from Japan’s International Space Station resupply ship H-IIB Transfer Vehicle (HTV) for its 3,800kg (fuelled) PM and 5,000kg OHM. Examples include the engines, the Environmental Control and Life Support Systems (ECLSS), electrical power network and avionics. However JAXA expects to have to find some mass savings in the HTV systems
The OHM would also provide life support for the 5,000kg MRM during periods on-orbit. This would enable the MRM ECLSS to be smaller. JAXA flight tested its Orbital Re-Entry Flight Experiment in 1994 and this would aid the MRM’s development. No final decision has been taken on the MRM’s shape but the agency wants to employ controlled lift for a lift/drag ratio of 0.4
The LES is 3,000kg making up the final 16,800kg figure. Like Soyuz JAXA’s spacecraft will abort with its habitation module attached meaning it will probably require the four folding drag plates that are used to control the aborting Soyuz’s aerodynamics before its parachute controlled descent starts
In an odd change to the norm JAXA wants, understandably, to have its MRM in the normal launch orientation but then on orbit to use a mechanical guidance “rail and wheel system” to move the RM forwards, round and back so it can ‘dock’ with its OHM
JAXA envisages four demonstration flights, two unmanned and two manned. The first demonstrates the MRM’s re-entry performance, the second the LES, and the operational H-IIA rocket could be used for these. The third is a manned on-orbit demonstration and the fourth is a full mission and both would need the H-IIB
The LEO mission would involve two or three days to reach the space station and then an on-orbit capability of one to two further weeks. JAXA rules out a lunar mission as it’s beyond the H-IIB’s “launch capability”. What no double launch mission?
Like China’s orbital module JAXA envisages its OHM as potentially becoming an additional module for a space station